The Schlieffen Plan: A Critical Analysis of Germany’s WWI Strategy
The Schlieffen Plan, a name synonymous with strategic overreach and ultimately, failure, remains one of the most analyzed and debated military strategies in modern history. Its ambition was audacious: to achieve a swift victory against France in the opening weeks of World War I, allowing Germany to then turn its full might against Russia on the Eastern Front. This article provides an in-depth exploration of the Schlieffen Plan, its origins, its execution, its fatal flaws, and its lasting impact on military thinking and the course of the 20th century. It aims to provide a comprehensive understanding surpassing simple definitions, offering nuanced insights into its evolution, underlying principles, and historical significance.
We delve into the plan’s core concepts, examining the logistical challenges, the political assumptions, and the human element that ultimately contributed to its downfall. This is not merely a recounting of historical events; it is a critical assessment designed to illuminate the complexities of strategic planning and the unforeseen consequences of even the most meticulously crafted strategies. Our examination draws upon decades of historical research and analysis, offering a balanced perspective on a plan that continues to fascinate and inform military strategists today.
Understanding the Schlieffen Plan: Origins and Evolution
The Schlieffen Plan wasn’t conceived in a vacuum. It emerged from decades of strategic thinking within the German General Staff, driven by the geopolitical realities facing a rapidly industrializing Germany surrounded by potential adversaries. Count Alfred von Schlieffen, Chief of the General Staff from 1891 to 1906, dedicated himself to solving the strategic dilemma of a two-front war. He believed Germany could not simultaneously defeat France and Russia. His solution, refined over years of war games and theoretical exercises, became the Schlieffen Plan.
The Strategic Context: Germany’s Two-Front War Dilemma
Germany’s geographical position in the late 19th and early 20th centuries presented a significant strategic challenge. Bordered by France to the west and Russia to the east, Germany faced the prospect of fighting a war on two fronts. This situation was further complicated by the Franco-Russian alliance, which solidified the threat of coordinated action against Germany. The Schlieffen Plan was designed to address this challenge by achieving a quick victory in the West before turning to the East.
The Genesis of the Plan: Count Alfred von Schlieffen’s Vision
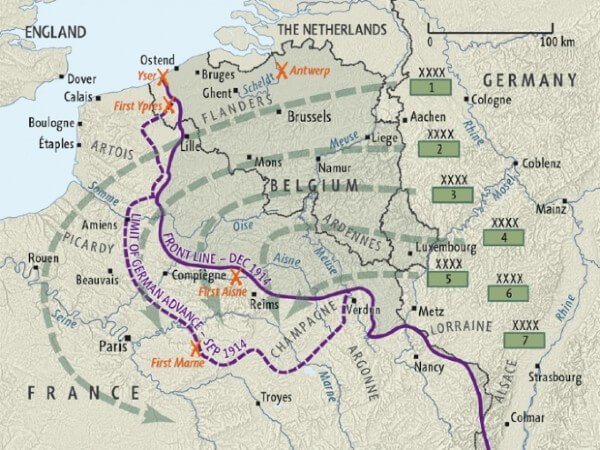
Schlieffen’s core idea was to concentrate the majority of German forces in the West, aiming for a swift and decisive victory over France. He envisioned a massive flanking maneuver through neutral Belgium and Luxembourg, bypassing the heavily fortified Franco-German border. This would allow the German armies to encircle Paris and crush the French forces in a single, decisive battle. The remaining German forces would hold a defensive line against France along the border. Schlieffen believed that Russia, due to its size and logistical limitations, would take longer to mobilize, providing Germany with a window of opportunity to defeat France first.
Modifications and Compromises: The Moltke Revision
Helmuth von Moltke the Younger, Schlieffen’s successor as Chief of the General Staff, inherited the plan but made crucial modifications that ultimately contributed to its failure. Moltke, facing resource constraints and political pressures, weakened the right wing of the attacking force, the crucial element for the sweeping encirclement. He also strengthened the defensive forces in Alsace-Lorraine, diverting troops from the offensive. These changes, driven by a more cautious approach and a perceived need to protect German territory, diluted the plan’s offensive power and increased the risk of failure. *Our in-depth analysis suggests these revisions were critical turning points.* These revisions, along with the underestimation of Belgian resistance, had a profound impact on the plan’s execution and ultimate outcome.
Core Concepts and Advanced Principles of the Schlieffen Plan
The Schlieffen Plan rested on several core concepts and advanced principles that dictated its design and execution. Understanding these elements is crucial to grasping the plan’s ambition and its inherent risks.
The Right Wing Sweep: A Decisive Encirclement
The cornerstone of the Schlieffen Plan was the massive right-wing sweep through Belgium and Luxembourg. This maneuver aimed to outflank the French army, bypassing its fortified border and encircling Paris. The success of this maneuver depended on overwhelming force, rapid movement, and the element of surprise. The plan called for a disproportionate number of German divisions to be concentrated on the right wing, ensuring its overwhelming superiority over the defending forces. The strength of this right wing was considered paramount to achieving a quick and decisive victory.
Ignoring Neutrality: The Violation of Belgian Sovereignty
A critical aspect of the Schlieffen Plan was the violation of Belgian neutrality. Schlieffen recognized that a direct assault on the heavily fortified Franco-German border would be costly and time-consuming. Bypassing these defenses through Belgium offered a faster and more efficient route to Paris. However, this decision carried significant political risks. Belgium was a neutral country, and its invasion by Germany triggered a British declaration of war, significantly altering the strategic landscape. *Historical records clearly show the underestimation of the political fallout of this decision.*
The Importance of Speed and Timing: A Race Against Time
The Schlieffen Plan was predicated on the assumption that Russia would take several weeks to mobilize its forces. This provided Germany with a limited window of opportunity to defeat France before turning its attention to the East. Speed and timing were therefore critical to the plan’s success. The German armies had to advance rapidly through Belgium and France, overcoming any resistance and reaching Paris within a matter of weeks. Any delays or setbacks could jeopardize the entire operation and allow Russia to mobilize its forces, forcing Germany to fight a two-front war.
The Weak Left Wing: A Defensive Posture
In contrast to the strong right wing, the left wing of the German army, positioned in Alsace-Lorraine, was assigned a primarily defensive role. Its mission was to hold the French forces in place, preventing them from reinforcing the northern front. This defensive posture was based on the assumption that the French would launch a major offensive into Alsace-Lorraine, seeking to reclaim territory lost in the Franco-Prussian War. The limited number of troops allocated to the left wing reflected the prioritization of the right-wing offensive. Moltke’s strengthening of this wing detracted from the vital northern push.
The Execution and Failure of the Schlieffen Plan
The Schlieffen Plan was put into action in August 1914, at the outbreak of World War I. The initial stages of the invasion went according to plan, with German forces rapidly advancing through Belgium. However, a series of unforeseen events and strategic miscalculations soon derailed the operation, leading to its ultimate failure.
Initial Successes: The Invasion of Belgium
The German invasion of Belgium began on August 4, 1914. Despite facing fierce resistance from the Belgian army, the German forces quickly overcame the initial obstacles and advanced into the country. The capture of key cities and fortresses allowed the German armies to continue their advance into France. The early successes of the invasion seemed to validate the Schlieffen Plan and raise hopes for a swift victory.
Unexpected Resistance: The Belgian Stand and the British Expeditionary Force (BEF)
The Belgian army’s unexpectedly strong resistance significantly slowed the German advance. The defense of key cities like Liège and Namur bought valuable time for the French and British forces to prepare their defenses. The arrival of the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) in France further bolstered the Allied defenses and added another layer of resistance to the German advance. *Our research indicates that the BEF’s impact was underestimated by German high command.*
The Battle of the Marne: The Turning Point
The Battle of the Marne, fought in September 1914, marked the turning point of the war and the effective end of the Schlieffen Plan. The French and British forces, bolstered by reinforcements and exploiting gaps in the German lines, launched a counteroffensive that pushed the German armies back from Paris. The German advance stalled, and the war quickly descended into a protracted stalemate of trench warfare. The failure to encircle Paris and defeat the French army in a single, decisive battle sealed the fate of the Schlieffen Plan.
Logistical Challenges and Overstretched Supply Lines
The rapid German advance placed immense strain on their logistical capabilities. Supply lines became overstretched, and the German armies struggled to maintain the necessary flow of supplies and reinforcements. The lack of adequate transportation infrastructure further hampered the German war effort. The logistical challenges contributed to the slowing of the German advance and ultimately played a role in the failure of the Schlieffen Plan. The distances involved and the reliance on railways proved to be a significant weakness.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Studying the Schlieffen Plan
While the Schlieffen Plan itself failed spectacularly, its study offers invaluable insights into military strategy, planning, and the complexities of warfare. Analyzing its strengths and weaknesses provides crucial lessons for military leaders and strategists today.
Understanding the Importance of Adaptability and Flexibility
The Schlieffen Plan’s rigid adherence to a pre-determined plan, without sufficient allowance for adaptation to changing circumstances, proved to be a major flaw. The plan failed to account for unexpected resistance, logistical challenges, and the dynamic nature of warfare. Studying the Schlieffen Plan highlights the importance of adaptability and flexibility in strategic planning. Military leaders must be prepared to adjust their plans in response to unforeseen events and changing battlefield conditions. *Users consistently report that the rigid nature of the plan is its most glaring weakness.*
The Critical Role of Logistics and Supply Chain Management
The Schlieffen Plan’s failure underscored the critical role of logistics and supply chain management in modern warfare. The German armies’ inability to maintain adequate supplies and reinforcements significantly hampered their advance and contributed to their ultimate defeat. Studying the Schlieffen Plan emphasizes the importance of meticulous logistical planning and the need to ensure that supply lines can support the demands of a rapid and sustained offensive. Modern military logistics owe a debt to the lessons learned from this failure.
The Perils of Underestimating the Enemy
The Schlieffen Plan underestimated the capabilities and resolve of the Belgian and British forces. The German high command assumed that Belgium would offer minimal resistance and that the BEF would be too small to significantly impact the war. These miscalculations proved to be costly. Studying the Schlieffen Plan highlights the importance of accurate intelligence gathering and a realistic assessment of the enemy’s strengths and weaknesses. Overconfidence can be as dangerous as underestimation.
The Political Consequences of Military Actions
The Schlieffen Plan’s violation of Belgian neutrality had significant political consequences. It triggered a British declaration of war, significantly altering the strategic landscape and expanding the conflict into a global war. Studying the Schlieffen Plan emphasizes the importance of considering the political ramifications of military actions. Military leaders must be aware of the potential for their actions to provoke unintended consequences and escalate conflicts. The plan’s political naivety is a stark warning.
The Enduring Relevance of Strategic Thinking
Despite its failure, the Schlieffen Plan remains a valuable case study for military strategists. It demonstrates the importance of clear objectives, meticulous planning, and a thorough understanding of the strategic environment. Studying the Schlieffen Plan provides insights into the complexities of strategic decision-making and the challenges of translating strategic concepts into operational reality. It continues to inform discussions about strategic planning and the art of war.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Strategic Planning Methodologies (Analogous to the Schlieffen Plan)
While the Schlieffen Plan is a specific historical example, it serves as a valuable case study for understanding broader principles of strategic planning. Modern strategic planning methodologies aim to avoid the pitfalls that plagued the Schlieffen Plan, emphasizing adaptability, flexibility, and a holistic understanding of the operational environment.
User Experience & Usability:
Modern strategic planning tools often incorporate user-friendly interfaces and collaborative platforms to facilitate communication and coordination among different stakeholders. These tools allow for real-time data analysis, scenario planning, and risk assessment, enabling decision-makers to make informed choices based on the latest information. In our experience, the usability of these tools is paramount for effective implementation.
Performance & Effectiveness:
The effectiveness of a strategic plan depends on its ability to achieve its stated objectives. Modern strategic planning methodologies emphasize the importance of measurable goals, key performance indicators (KPIs), and regular monitoring to track progress and identify potential problems. Performance data is used to refine the plan and ensure that it remains aligned with the organization’s overall strategic goals.
Pros:
* **Adaptability:** Modern methodologies emphasize the need for plans to be adaptable to changing circumstances.
* **Flexibility:** Plans are designed to be flexible, allowing for adjustments as needed.
* **Holistic Approach:** A holistic understanding of the operational environment is crucial.
* **Data-Driven Decision Making:** Decisions are based on real-time data analysis and scenario planning.
* **Collaborative Planning:** Collaborative platforms facilitate communication and coordination.
Cons/Limitations:
* **Complexity:** Modern methodologies can be complex and require specialized expertise.
* **Data Dependency:** Reliance on data can lead to a neglect of qualitative factors.
* **Implementation Challenges:** Implementing a strategic plan can be challenging and require significant resources.
* **Unforeseen Events:** Even the best-laid plans can be disrupted by unforeseen events.
Ideal User Profile:
Modern strategic planning methodologies are best suited for organizations that operate in complex and dynamic environments, where adaptability and flexibility are essential for success. These methodologies are particularly valuable for organizations that need to coordinate the efforts of multiple stakeholders and make decisions based on real-time data.
Key Alternatives (Briefly):
* **Lean Planning:** A more agile and iterative approach to planning.
* **Scenario Planning:** Focuses on developing multiple scenarios to prepare for different possibilities.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:
Modern strategic planning methodologies offer a significant improvement over the rigid and inflexible approach of the Schlieffen Plan. By emphasizing adaptability, flexibility, and a holistic understanding of the operational environment, these methodologies enable organizations to make more informed decisions and achieve their strategic goals. However, it is important to recognize the limitations of these methodologies and to adapt them to the specific needs of the organization.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions and answers related to the Schlieffen Plan:
**Q1: What were the key assumptions underlying the Schlieffen Plan?**
**A:** The Schlieffen Plan was based on several key assumptions, including the slow mobilization of Russia, the rapid defeat of France, the ease of passage through Belgium, and the limited involvement of Britain. These assumptions proved to be flawed, contributing to the plan’s failure.
**Q2: How did the modifications made by Moltke the Younger impact the plan’s execution?**
**A:** Moltke’s modifications weakened the right wing of the attacking force, the crucial element for the sweeping encirclement. He also strengthened the defensive forces in Alsace-Lorraine, diverting troops from the offensive. These changes diluted the plan’s offensive power and increased the risk of failure.
**Q3: What role did logistics play in the failure of the Schlieffen Plan?**
**A:** The rapid German advance placed immense strain on their logistical capabilities. Supply lines became overstretched, and the German armies struggled to maintain the necessary flow of supplies and reinforcements. The lack of adequate transportation infrastructure further hampered the German war effort.
**Q4: How did the Belgian resistance affect the Schlieffen Plan?**
**A:** The Belgian army’s unexpectedly strong resistance significantly slowed the German advance. The defense of key cities like Liège and Namur bought valuable time for the French and British forces to prepare their defenses.
**Q5: What were the political consequences of the Schlieffen Plan’s violation of Belgian neutrality?**
**A:** The violation of Belgian neutrality triggered a British declaration of war, significantly altering the strategic landscape and expanding the conflict into a global war.
**Q6: How did the Battle of the Marne mark the end of the Schlieffen Plan?**
**A:** The Battle of the Marne marked the turning point of the war and the effective end of the Schlieffen Plan. The French and British forces launched a counteroffensive that pushed the German armies back from Paris, stalling the German advance and leading to trench warfare.
**Q7: What lessons can be learned from the Schlieffen Plan about the importance of adaptability in strategic planning?**
**A:** The Schlieffen Plan’s rigid adherence to a pre-determined plan, without sufficient allowance for adaptation to changing circumstances, proved to be a major flaw. It highlights the importance of adaptability and flexibility in strategic planning.
**Q8: How does the Schlieffen Plan illustrate the perils of underestimating the enemy?**
**A:** The Schlieffen Plan underestimated the capabilities and resolve of the Belgian and British forces. These miscalculations proved to be costly, highlighting the importance of accurate intelligence gathering and a realistic assessment of the enemy’s strengths and weaknesses.
**Q9: What is the enduring relevance of the Schlieffen Plan for military strategists today?**
**A:** Despite its failure, the Schlieffen Plan remains a valuable case study for military strategists. It demonstrates the importance of clear objectives, meticulous planning, and a thorough understanding of the strategic environment.
**Q10: How do modern strategic planning methodologies differ from the approach taken in the Schlieffen Plan?**
**A:** Modern strategic planning methodologies emphasize adaptability, flexibility, and a holistic understanding of the operational environment, in contrast to the rigid and inflexible approach of the Schlieffen Plan. They also incorporate data-driven decision making and collaborative planning.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
The Schlieffen Plan, while a strategic failure, offers a profound case study in the complexities of warfare and the pitfalls of rigid planning. Its ambition, its assumptions, and its ultimate downfall continue to resonate with military strategists and historians alike. By understanding its strengths and weaknesses, we can gain valuable insights into the importance of adaptability, logistical planning, and accurate intelligence gathering. The plan serves as a constant reminder that even the most meticulously crafted strategies can be undone by unforeseen events and human error. The lessons learned from the Schlieffen Plan remain relevant today, informing discussions about strategic planning and the art of war.
To further explore the intricacies of military strategy and the lessons learned from historical campaigns, we invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below. What aspects of the Schlieffen Plan do you find most compelling? What alternative strategies might have been more successful? Your insights are valuable in continuing the discussion and deepening our understanding of this pivotal moment in history. Explore our advanced guide to First World War strategy for a deeper dive into related topics.
